Quarterly Financial Report for the quarter ended September 30, 2024
Statement outlining results, risks, and significant changes in
operations, personnel, and program
1. Introduction
This Quarterly Financial Report (QFR) has been prepared by management as required by section 65.1 of the Financial Administration Act and in the form and manner prescribed by the Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat. This QFR should be read in conjunction with the Main Estimates and Supplementary Estimates. It has not been subject to an external audit or review.
1.1 Mandate
The Office of the Commissioner for Federal Judicial Affairs (FJA) Canada was created in 1978 under the authority of the Judges Act to safeguard the independence of the judiciary and in order to put federally appointed judges at arm’s length from the administration of the Department of Justice. FJA’s mandate extends to promoting better administration of justice and providing support for the federal judiciary.
FJA administers three distinct and separate components that are funded from different sources. Statutory funding is allocated for the judges’ salaries, allowances and annuities, and surviving beneficiaries’ benefits. Voted appropriations are provided in two separate votes to support the administrative activities of FJA and the Canadian Judicial Council (CJC).
Under the Departmental Results Framework, the organization’s core responsibility is to provide support to federally appointed judges. In addition to Internal Services, the organization is broken down into three program activities: payments pursuant to the Judges Act, FJA, and CJC.
Further details about FJA’s authority, mandate, and programs can be found below and in FJA’s Departmental Plan, Main Estimates and Supplementary Estimates located on FJA’s and the Treasury Board’s websites at www.fja-cmf.gc.ca and www.tbs-sct.gc.ca.
1.2 Basis of Presentation
This quarterly report has been prepared using an expenditure basis of accounting. The accompanying Statement of Authorities includes FJA’s spending authorities granted by Parliament and those used by the department consistent with the Main Estimates for the 2024-2025 fiscal year. This quarterly report has been prepared using a special purpose financial reporting framework designed to meet financial information needs with respect to the use of spending authorities.
The authority of Parliament is required before money can be spent by the Government. Approvals are given in the form of annually approved limits through appropriation acts or through legislation in the form of statutory spending authority for specific purposes.
When Parliament is dissolved for the purposes of a general election, section 30 of the Financial Administration Act authorizes the Governor General, under certain conditions, to issue a special warrant authorizing the Government to withdraw funds from the Consolidated Revenue Fund. A special warrant is deemed to be an appropriation for the fiscal year in which it is issued.
FJA uses the full accrual method of accounting to prepare and present its annual departmental financial statements that are part of the departmental results reporting process. However, the spending authorities voted by Parliament remain on an expenditure basis.
2. Highlights of fiscal quarter and fiscal year to date (YTD) results
FJA is financed by the Government through Parliamentary Appropriations (e.g. Statutory Authorities for payments pursuant to the Judges Act and Employee Benefits Plans (EBP) and Voted Authorities to support the administration of FJA and CJC).
Vote-netting is a means of funding selected programs or activities wherein Parliament authorizes FJA to apply revenues collected towards costs directly incurred for specific activities. FJA has the authority to spend revenues received during the year arising from the provision of administrative services.
This QFR reflects the results of the current fiscal period in relation to the authorities available as at September 30, 2024.
Changes to Departmental Authorities
As at September 30, 2024, the total authorities available to FJA are $55.3 million higher compared with the same quarter last fiscal year. This net increase is comprised of:
- An increase of $54.7 million in statutory authorities for judges’ salaries, allowances and annuities, as well as for contributions to employee benefit plans.
- An increase of $0.6 million in voted authorities for the department’s operating budget.
Changes to Budgetary Expenditures
As at September 30, 2024, the department’s total net budgetary expenditures increased by $25.5 million (a $26 million increase in Statutory Expenditures for payments pursuant to the Judges Act and EBP, and a $0.5 million decrease in Voted Expenditures to support the administration of FJA and CJC) compared with the same quarter last fiscal year. This variance is comprised of:
- A year-to-date net increase of $23.3 million in personnel expenditures (including EBP).
- A year-to-date net increase of $1.3 million in transportation and telecommunications expenditures.
- A year-to-date net increase of $0.8 million in professional services expenditures.
- An overall net increase of $0.1 million for all other non-salary expenditures.
Figure 1: Comparison of Authorities Granted and Used (in thousands of dollars)
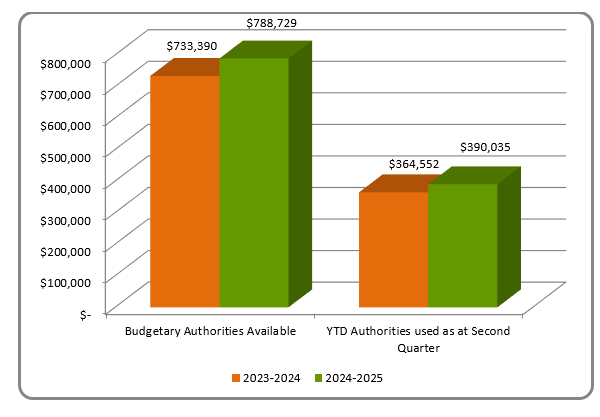
The chart illustrates the variation in thousands of dollars of the annual budgetary authorities granted and used as at September 30, 2023 and 2024.
As at September 30, 2023 and 2024, FJA’s total authorities available were $733,390,367 in 2023-2024 and $788,728,803 in 2024-2025. Authorities used as at the second quarter totalled $364,551,608 in 2023-2024 and $390,034,593 in 2024-2025.
3. Risks and Uncertainties
FJA’s environment is complex due to the range of services it provides and the large number of clients served. Recognizing this context, FJA has developed a risk profile and actively monitors internal and external risks through its management team.
FJA continues agile management of its resources to shift and reallocate resources to adapt to emerging needs as required.
4. Significant changes in relation to operations, personnel and programs
As at September 30, 2024, the significant increase in expenses related to transportation and professional services compared with the same quarter last fiscal year is primarily attributable to court-related travel and attendance at conferences, impacted by the increase in airfare, hotel rates (including accommodation and large room rentals) and other such costs.
5. Approval by Senior Officials
Approved by:
Original signed by:
Marc A. Giroux
Commissioner
Ottawa (Canada)
Date: November 25, 2024
Original signed by:
Errolyn Humphreys
Chief Financial Officer
Ottawa (Canada)
Date: November 25, 2024
Statement of Authorities (unaudited)
Fiscal year 2024-2025 (in thousands of dollars)
|
|
Total available for use for the year ending |
Used during the quarter ended |
Year- to-date used at quarter-end |
|
Vote 1 – FJA – Operating expenditures |
11,011 |
2,859 |
5,154 |
|
Vote 5 – CJC – Operating expenditures |
2,881 |
465 |
874 |
|
Less: Vote 1 – FJA – Revenues |
(275) |
- |
- |
|
Net operating expenditures |
13,617 |
3,324 |
6,028 |
|
Statutory authorities – EBP |
1,049 |
262 |
524 |
|
Statutory authorities – Judges salaries, allowances and annuities |
774,063 |
194,983 |
383,483 |
|
Total budgetary authorities |
$ 788,729 |
$ 198,569 |
$ 390,035 |
*Includes only Authorities available for use and granted by Parliament at quarter-end.
Fiscal year 2023-2024 (in thousands of dollars)
|
|
Total available for use for the year ending |
Used during the quarter ended |
Year- to-date used at quarter-end |
|
Vote 1 – FJA – Operating expenditures |
10,414 |
2,908 |
5,543 |
|
Vote 5 – CJC – Operating expenditures |
2,872 |
504 |
947 |
|
Less: Vote 1 – FJA – Revenues |
(275) |
- |
- |
|
Net operating expenditures |
13,011 |
3,412 |
6,490 |
|
Statutory authorities – EBP |
1,064 |
266 |
532 |
|
Statutory authorities – Judges salaries, allowances and annuities |
719,315 |
181,289 |
357,530 |
|
Total budgetary authorities |
$ 733,390 |
$ 184,967 |
$ 364,552 |
*Includes only Authorities available for use and granted by Parliament at quarter-end.
Departmental budgetary expenditures by Standard Object (unaudited)
Fiscal year 2024-2025 (in thousands of dollars)
|
Planned expenditures for the year ending |
Expended during the quarter ended |
Year-to-date used at quarter-end |
|
|
Expenditures |
|||
|
Personnel - including EBP |
737,349 |
186,867 |
362,672 |
|
Transportation and communications |
21,869 |
5,252 |
12,171 |
|
Information |
154 |
32 |
61 |
|
Professional and special services |
19,914 |
4,650 |
9,459 |
|
Rentals |
989 |
237 |
419 |
|
Repair and maintenance |
56 |
16 |
27 |
|
Utilities, materials and supplies |
11 |
5 |
6 |
|
Acquisition of machinery and equipment |
29 |
3 |
13 |
|
Other subsidies and payments |
8,633 |
1,507 |
5,207 |
|
Total gross budgetary expenditures |
789,004 |
198,569 |
390,035 |
|
Less revenues netted against expenditures |
|||
|
Revenues |
(275) |
- |
- |
|
Total net budgetary expenditures |
$ 788,729 |
$ 198,569 |
$ 390,035 |
Fiscal year 2023-2024 (in thousands of dollars)
|
Planned expenditures for the year ending March 31, 2024 |
Expended during the quarter ended September 30, 2023 |
Year-to-date used at quarter-end |
|
|
Expenditures |
|||
|
Personnel - including EBP |
684,012 |
173,486 |
339,350 |
|
Transportation and communications |
25,578 |
4,958 |
10,852 |
|
Information |
135 |
18 |
45 |
|
Professional and special services |
13,065 |
4,684 |
8,635 |
|
Rentals |
656 |
290 |
445 |
|
Repair and maintenance |
52 |
1 |
15 |
|
Utilities, materials and supplies |
66 |
2 |
3 |
|
Acquisition of machinery and equipment |
462 |
1 |
37 |
|
Other subsidies and payments |
9,639 |
1,527 |
5,170 |
|
Total gross budgetary expenditures |
733,665 |
184,967 |
364,552 |
|
Less revenues netted against expenditures |
|||
|
Revenues |
(275) |
- |
- |
|
Total net budgetary expenditures |
$ 733,390 |
$ 184,967 |
$ 364,552 |
- Date modified: